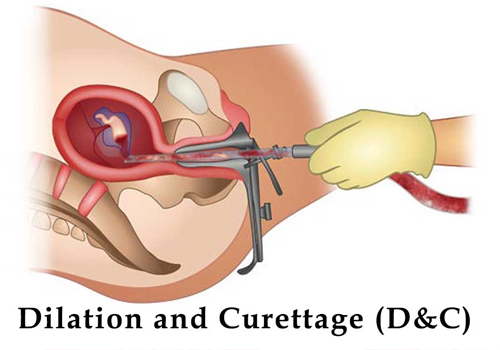
D&C
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a minor surgical procedure performed to remove tissue from the uterus. It is often used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, depending on the patient’s condition.
What Happens During a D&C?
-
Preparation:
- Anesthesia: The procedure is typically done under local, regional, or general anesthesia to ensure patient comfort.
- Cervical Dilation: The cervix is gradually dilated using medications or dilators to allow access to the uterus.
-
Curettage:
- A thin instrument (curette) is inserted into the uterus to gently scrape or suction out uterine tissue.
-
Completion:
- The collected tissue may be sent to a lab for analysis if required (e.g., to check for abnormalities or confirm a miscarriage).
Reasons for a D&C
-
Diagnostic Purposes:
- To investigate abnormal uterine bleeding.
- To diagnose uterine conditions, such as fibroids, polyps, or cancer.
- To confirm the presence of certain reproductive conditions, like endometrial hyperplasia.
-
Therapeutic Purposes:
- To remove remaining tissue after a miscarriage or abortion.
- To treat heavy or prolonged bleeding.
- To clear out the uterine lining in cases of incomplete miscarriage or molar pregnancy.
- To remove placental fragments after childbirth.
Procedure Duration
- The procedure typically lasts 10-20 minutes, but patients may need a few hours at the clinic or hospital for preparation and recovery.
Post-Procedure Recovery
-
Physical Recovery:
- Mild cramping and light bleeding may occur for a few days.
- Most women can resume normal activities within a day or two.
-
Follow-Up Care:
- Avoid inserting anything into the vagina (e.g., tampons, douching) or sexual activity for about 1-2 weeks to reduce infection risk.
- Follow the healthcare provider’s advice on managing pain and other symptoms.
-
Watch for Complications:
- Contact your doctor if you experience heavy bleeding, fever, severe pain, or foul-smelling discharge, as these may indicate an infection or other complications.
Risks of a D&C
- Infections: Rare but possible if bacteria enter the uterus during the procedure.
- Uterine Perforation: Rare; occurs if the instrument punctures the uterine wall.
- Cervical Damage: May occur during dilation.
- Asherman’s Syndrome: Rare scarring of the uterus that may affect future fertility.
- Bleeding: Usually mild, but heavy bleeding may occur in rare cases.
When is a D&C Recommended?
- D&C is advised when less invasive treatments are ineffective or when precise tissue removal or diagnosis is necessary.

