Orchidectomy & Hydrocoele repair
Orchidectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of one or both testicles. It is typically performed for medical conditions such as testicular cancer, severe trauma, or as part of gender-affirming surgery.
Indications for Orchidectomy
- Testicular Cancer: To remove a cancerous testicle and prevent the spread of cancer.
- Trauma: In cases of irreparable testicular injury.
- Chronic Infections or Torsion: If the testicle is severely damaged due to infection or twisting.
- Gender-Affirming Surgery: As part of male-to-female transition.
- Hormonal Treatment for Prostate Cancer: In some cases, to reduce testosterone production.
Procedure
- Anesthesia:
- Performed under general or spinal anesthesia.
- Incision:
- A small incision is made in the groin or scrotum.
- Dissection and Removal:
- The testicle is carefully separated from surrounding tissues, including blood vessels and the spermatic cord, and then removed.
- Closure:
- The incision is closed with sutures. In some cases, a prosthetic testicle may be inserted to maintain appearance.
Postoperative Care
- Pain Management: Mild to moderate pain is managed with analgesics.
- Swelling and Bruising: Ice packs are recommended for the first 24-48 hours.
- Catheter Care: If a catheter is placed, it is removed after a short period.
- Recovery Time: Most patients can return to light activities within 1–2 weeks but should avoid strenuous exercise for about 4–6 weeks.
Risks and Complications
- Bleeding or hematoma (blood collection).
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Damage to surrounding structures (e.g., vas deferens, blood vessels).
- Psychological Impact: Some individuals may experience emotional distress or concerns about body image.
- Loss of Fertility: Removal of both testicles results in infertility, though sperm banking can be an option prior to surgery.
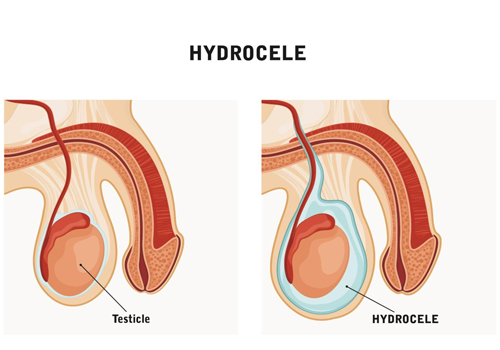
Hydrocoele Repair
A hydrocoele is a fluid-filled sac surrounding the testicle, causing scrotal swelling. Hydrocoele repair is a surgical procedure to remove or drain the fluid and repair the sac.
Indications for Hydrocoele Repair
- Pain or discomfort due to the enlarged scrotum.
- Cosmetic concerns with noticeable swelling.
- Hydrocoele increasing in size, especially in adults.
- Infection or inflammation of the hydrocoele.
- Infertility: Rare, but in some cases, it may affect fertility if left untreated.
Procedure
- Anesthesia:
- Performed under general or regional anesthesia (spinal or local anesthesia with sedation).
- Incision:
- A small incision is made in the scrotum or lower abdomen, depending on the location of the hydrocoele.
- Fluid Drainage:
- The hydrocoele sac is opened, and the fluid is drained.
- Sac Removal or Plication:
- The hydrocoele sac may be removed or plicated (folded and sutured to prevent further fluid accumulation).
- Closure:
- The incision is closed with sutures, and a drain may be placed temporarily to prevent fluid buildup.
Postoperative Care
- Pain Management: Mild discomfort is managed with analgesics.
- Swelling: Swelling of the scrotum is common after surgery, but it usually resolves within 1–2 weeks.
- Activity: Rest for a few days, avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activity for several weeks.
- Follow-up: Regular follow-up visits to check for any recurrence or complications.
Risks and Complications
- Infection at the incision site.
- Bleeding or hematoma formation.
- Recurrence of the hydrocoele.
- Damage to the testicle or other surrounding structures.
- Testicular atrophy or shrinkage in rare cases.
Comparison of Orchidectomy and Hydrocoele Repair
| Procedure | Orchidectomy | Hydrocoele Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Indication | Testicular cancer, trauma, or gender-affirming surgery | Fluid-filled sac around the testicle causing swelling or discomfort |
| Surgical Approach | Removal of the testicle | Drainage and/or removal of the hydrocoele sac |
| Anesthesia | General or spinal anesthesia | General or regional anesthesia |
| Recovery | 1–2 weeks for light activities; 4–6 weeks for heavy activities | 1–2 weeks for light activities; 4–6 weeks for heavy activities |
| Complications | Bleeding, infection, psychological effects | Infection, bleeding, recurrence of hydrocoele |
| Outcome | Fertility loss (if both testicles removed), cosmetic changes | Swelling relief, potential recurrence |
Both orchidectomy and hydrocoele repair are generally safe procedures with high success rates, but they require appropriate preoperative counseling and postoperative care to avoid complications and ensure optimal outcomes.

