Vaginitis & cervicitis
Vaginitis and cervicitis are common gynecological conditions that involve inflammation or infection of the vagina and cervix, respectively. These conditions can cause discomfort, abnormal discharge, and other symptoms. Here's a detailed overview:
Vaginitis
Definition:
Inflammation or infection of the vagina caused by microbial imbalance, irritants, or infections.
Causes:
-
Infections:
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): Overgrowth of harmful bacteria, disrupting the normal vaginal flora.
- Yeast Infection: Caused by Candida albicans, a fungus.
- Trichomoniasis: A sexually transmitted infection caused by Trichomonas vaginalis.
-
Non-Infectious Causes:
- Allergies or irritation from products like soaps, douches, or spermicides.
- Hormonal changes (e.g., during menopause, pregnancy, or breastfeeding).
Symptoms:
- Vaginal discharge (may be thick, thin, or foul-smelling).
- Itching or irritation.
- Burning sensation, especially during urination.
- Pain or discomfort during intercourse.
- Redness or swelling of the vaginal area.
Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination: To assess signs of inflammation.
- Lab Tests: Vaginal swab to identify the causative organism.
- pH Testing: Vaginal pH is higher in certain infections like BV or trichomoniasis.
Treatment:
-
Bacterial Vaginosis:
- Antibiotics (e.g., metronidazole or clindamycin).
-
Yeast Infection:
- Antifungal creams, suppositories, or oral medications (e.g., fluconazole).
-
Trichomoniasis:
- Oral antibiotics (e.g., metronidazole or tinidazole).
-
Non-Infectious Vaginitis:
- Avoid irritants and use prescribed corticosteroid creams if needed.
- Estrogen creams for hormonal-related vaginitis.
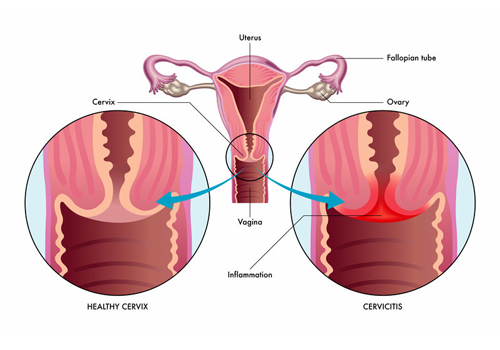
Cervicitis
Definition:
Inflammation of the cervix, often caused by infections or irritation.
Causes:
-
Infectious Causes:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as:
- Chlamydia (Chlamydia trachomatis).
- Gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae).
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV).
- Trichomoniasis.
- Bacterial overgrowth or imbalance (similar to BV).
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as:
-
Non-Infectious Causes:
- Chemical irritants (e.g., douches, contraceptive creams).
- Allergic reactions (e.g., latex in condoms).
Symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (may be yellow, green, or foul-smelling).
- Bleeding between periods or after intercourse.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort.
- Burning sensation during urination.
- In many cases, cervicitis can be asymptomatic.
Diagnosis:
- Pelvic Examination: Visualization of cervical inflammation or discharge.
- Pap Smear: Screening for abnormalities or infections.
- Culture or PCR Testing: To identify infectious organisms (e.g., chlamydia, gonorrhea).
Treatment:
-
Infectious Cervicitis:
- Antibiotics or antivirals based on the causative agent (e.g., azithromycin for chlamydia, acyclovir for herpes).
-
Non-Infectious Cervicitis:
- Avoidance of irritants or allergens.
- Corticosteroid creams for severe inflammation.
Prevention of Vaginitis and Cervicitis
- Practice safe sex (use condoms).
- Avoid excessive use of douches, perfumes, or harsh soaps in the genital area.
- Maintain proper hygiene.
- Wear breathable, cotton underwear.
- Get regular gynecological check-ups and STI screenings.
When to See a Doctor
- Persistent symptoms like unusual discharge, pelvic pain, or bleeding.
- Symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- Recurrent episodes of infections.

